Project 06
Optogenetic analysis of membrane compartmentalization between and within excitable cells
Principle Investigator: Prof. Dr. Alexander Gottschalk
Research Areas: Cell Physiology, Neuroscience
Summary
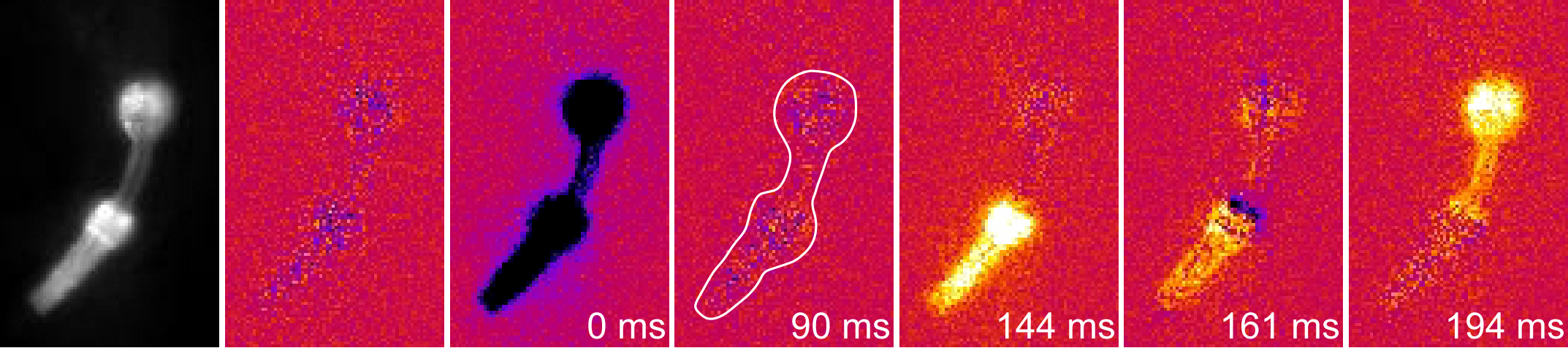
Networks of excitable cells are formed by electrical (gap) junctions. In project P06, we will address the role of gap junction subunits (and accessory stomatins) in muscular and nervous systems of an intact animal (Caenorhabditis elegans), using state-of-the-art optogenetic actuation and voltage imaging in closed-loop. This project will decipher such gap junction networks acting in muscular electrical compartmentalization, and in neural circuit function regulating behavior.

Prof. Dr. Alexander Gottschalk
06: PROJECT-RELATED PUBLICATIONS
- Rentsch D, Bergs A, Shao J, Elvers N, Ruse C, Seidenthal M, Aoki I, Gottschalk A* (2024) Tools and methods for cell ablation and cell inhibition in Caenorhabditis elegans. Genetics 229: iyae119
- Bergs ACF, Liewald JF, Rodriguez-Rozada S, Liu Q, Wirt C, Bessel A, Zeitzschel N, Durmaz H, Nozownik A, Vierock J, Bargmann CI, Hegemann P, Wiegert JS, Gottschalk A (2022) All-optical closed-loop voltage clamp for precise control of muscles and neurons in live animals. bioRxiv preprint
- Steuer Costa W, Van der Auwera P, Glock C, Liewald JF, Bach M, Schuler C, Wabnig S, Oranth A, Masurat F, Bringmann H, Schoofs L, Stelzer E, Fischer S, Gottschalk A (2019) A GABAergic and peptidergic sleep neuron as a locomotion stop neuron with compartmentalized Ca2+ dynamics. Nat Commun 10: 4095
- Azimi Hashemi N, Bergs ACF, Schuler C, Scheiwe AR, Steuer Costa W, Bach M, Liewald JF, Gottschalk A (2019) Rhodopsin-based voltage imaging tools for use in muscles and neurons of Caenorhabditis elegans. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 116: 17051-60
- Bergs A, Schultheis C, Fischer E, Tsunoda SP, Erbguth K, Husson SJ, Govorunova E, Spudich JL, Nagel G, Gottschalk A*, Liewald JF* (2018) Rhodopsin optogenetic toolbox v2.0 for light-sensitive excitation and inhibition in Caenorhabditis elegans. PLoS One 13: e0191802
- Oranth A, Schultheis C, Tolstenkov O, Erbguth K, Nagpal J, Hain D, Brauner M, Wabnig S, Steuer Costa W, McWhirter RD Zels S, Palumbos S, Miller Iii DM, Beets I, Gottschalk A (2018) Food sensation modulates locomotion by dopamine and neuropeptide signaling in a distributed neuronal network. Neuron 100: 1414-28
- Tolstenkov O, Van der Auwera P, Steuer Costa W, Bazhanova O, Gemeinhardt TM, Bergs AC, Gottschalk A (2018) Functionally asymmetric motor neurons contribute to coordinating locomotion of Caenorhabditis elegans. eLife 7: e34997
- Hermann A, Liewald JF, Gottschalk A (2015) A photosensitive degron enables acute light-induced protein degradation in the nervous system. Curr Biol 25: R749-R750
- Schuler C, Fischer E, Shaltiel L, Steuer Costa W, Gottschalk A (2015) Arrhythmogenic effects of mutated L-type Ca2+-channels on an optogenetically paced muscular pump in Caenorhabditis elegans. Sci Rep 5: 14427
- Akerboom J, Carreras Calderon N, Tian L, Wabnig S, Prigge M, Tolo J, Gordus A, Orger MB, Severi KE, Macklin JJ, Patel R, Pulver SR, Wardill TJ, Fischer E, Schüler C, Chen TW, Sarkisyan KS, Marvin JS, Bargmann CI, Kim DS, Kügler S, Lagnado L, Hegemann P, Gottschalk A, Schreiter ER, Looger LL (2013) Genetically encoded calcium indicators for multi-color neural activity imaging and combination with optogenetics. Front Mol Neurosci 6: 2
